Please feel free to contact us for additional information regarding your case.
|
Please feel free to contact us for additional information regarding your case. |
 Rock DrillingThe combined methods of drilling and broaching for the primary cut in quarrying; deep, closely spaced holes are drilled in a straight line by means of a reciprocating drill, and webs between holes are removed by an excavator mounted hydraulic breaker. |

Drilled Shoring PilesShoring is commonly used when installing the foundation of a building. A shoring system such as piles and lagging or shotcrete will support the surrounding loads until the underground levels of the building are constructed. |
 Soil NailSoil nailing is an economical technique for stabilizing slopes and for constructing retaining walls from the top down. This ground reinforcement process uses steel tendons which are drilled and grouted into the soil to create a composite mass similar to a gravity wall |
 "H" PilesH-Piles are designed for deep foundation applications. These piles transfer structural loads away from surface soils, which do not have the mechanical properites to support large buildings, to deeper bearing strata soils. H-piles are most commonly used in dense soils or rock where no piling system is better for offering pile resistance at the tip for point bearing capacity. This design includes a whaler with |
 Micro PilesMicropiles, also known as minipiles, (and less commonly as pin piles, needle piles, mini caisson and root piles) are deep foundation elements constructed using high-strength, small-diameter steel casing and/or threaded bar. Capacities vary depending on the micropile size and subsurface profile. The micropile casing generally has a diameter in the range of 8 to 12 inches. |

Mini CaissonThrust Drilling's micropile drill rigs allow installation in restricted access, low headroom interiors, permitting facility upgrades with minimal disruption to normal operations. Typically, the casing is advanced to the design depth using a drilling technique. Reinforcing steel in the form of an all-thread bar is typically inserted into the micropile casing. High-strength cement grout is then pumped into the casing. |
 Tie BackTieback anchors comprise a barrel anchorage located either in a bearing layer which is tensioned at the front face of the wall. The part of the anchor that transfers the force to the surrounding soil is frequently called the "fixed length". In some projects tiebacks have been used in combination with rakers and soil berms and/or corner braces. |
 Vibratory HammerVibratory Hammers are used to maintain synchronization and cancel horizontal vibration, paired eccentrics, powered by hydraulic motors, rotate in the gear case.Vibration is transmitted into a driven pile by means of a hydraulic clamp attached to the bottom of the gear case. |
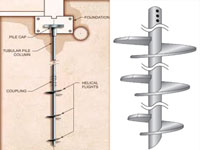 Helical Pile SystemThe helical pile system is a segmented deep foundation system with helical bearing plates welded to a central shaft. Load is transferred from the shaft to the soil through helical bearing plates. As a result of their true helical shape, the helices do not auger into the soil but rather screw into it with minimal disturbance. |
 Underpinning RepairDuring the underpinning process this building was undermined, the basement slab collapsed and the building split in several section. the nycdob condemned the building. the GC braced with, rakers, whalers and deadmen. We drilled every section of underpinning and high pressure grouted the entire length of the building. all voids were filled, the slab raised and the building was deamed stable for demolition. |

Low Headroom & Limited AccessWe have the experience and equipment for every application. |